This depends on the various elasticities that exist in the relevant markets. In other words according to this theory government spending may not succeed in increasing aggregate demand because private sector spending decreases as a result and in proportion to said government.
Economics In Plain English The Almighty Bond Market Niall Ferguson S Concerns About The Us Deficit Explained
A situation when increased interest rates lead to a reduction in private investment spending such that it dampens the initial increase of total investment spending is called crowding out effect.
. Crowding out refers to all the things which can go wrong when debt-financed fiscal policy is used to affect output. For example if the supply of loanable funds is elastic and the demand for capital is inelastic the impact of higher. Sometimes government adopts an expansionary fiscal policy stance and increases its spending to boost the economic activity.
In this model the effect of the fiscal policy is minimal and therefore the government should keep the budget close to the balance and avoid financial interventions in the economy. The crowding out effect is a prominent economic theory stating that increasing public sector spending has the effect of decreasing spending in the private sector. The main determinant of the extent to which crowding out takes place is the shape of the LM curve.
Borrowed money must eventually be paid back. A direct crowding-out effect may occur. Crowding out begins to take effect when the interest rate level reaches a.
Consider first the most-extreme case in which government borrowing has the exact same effect on the economy as government taxation. Romneys tax cuts according to the classical model will lead to the increase in consumption and to the decrease of investments due to the crowding-out effect. In economics crowding out is a phenomenon that occurs when increased government involvement in a sector of the market economy substantially affects the remainder of the market either on the supply or demand side of the market.
In the extreme the ultrarationality assumption would imply the complete crowding out of private contributions by governmental transfers. Crowding out effect is the consequence of changes made by the government to fiscal policy that affect private investment and consumption. Most government borrowing involves selling bonds.
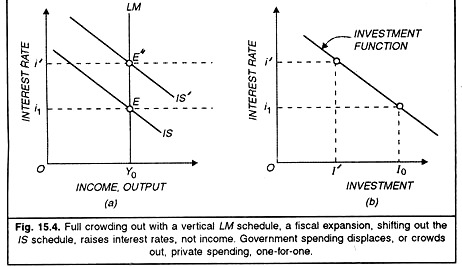
But if the LM curve is vertical complete crowding out occurs. Policy Effectiveness And the Slope of the LM Curve - Summary For the case of fiscal policy where the interest-rate response with the resulting crowding out of investment offsets part of the effect of the policy action the income response is greater the smaller the interest rate response. The theory behind the crowding out effect assumes that governmental borrowing uses up a larger and larger proportion of the total supply of savings available for investment.
Then if the government spending increases by 10 billion the investment later on decreases by 10 billion then which of the following is true. How Does Crowding Out Happen. To illustrate consider the individual who is allocating 100 of current income to charitable contributions.
Higher taxes mean consumers and companies have less left over to spend. Increase _____ occur when government spending competes with the private sector and is increased. This description of crowding-out and crowding-in and why crowding-in is likely to dominate in recessions is from Baumol and Blinders.
Effect of transactional crowding out is defined as the phenomenon of the decrease in private investment and private consumption resulting from an increase in the interest rates which is the consequence of fiscal stimulus see Keynes 2003 p. On the contrary the government expenditure may reduce private expenditure by less than the increase in government expenditure then the crowding out effect is partial or incomplete. Of course even if the crowding out effect exists it may be a weak effect.
Raising taxes or borrowing. In terms of absolute values a complete crowding-out effect occurs when the increase in government spending equals the decrease in investment. The government can boost spending by doing two things.
In this case private sector investment will not be adversely affected. Government borrowing can crowd out private spending and investment in a number of ways. This leads to an.
Because demand for savings increases while supply stays the same the price of money the interest rate goes up. In the extreme case of direct expenditure offsets the. The crowding out effect refers to a situation of high government expenditure supported by high borrowing causes decrease in private expenditure.
This is called the crowding-out effect. If the LM curve is horizontal that is if the demand for money is very sensitive to the interest rate crowding out does not occur and fiscal policy will have a large effect on output the Keynesian case. When government expenditure displaces or crowds out an equal amount of private expenditure the crowding out effect is said to be complete or total.
The _____ theorem holds that an increase in the government budget deficit has no. A first line of argument questions whether fiscal policy has any effect at all on spending. Resource crowding out occurs when the government uses up resources that would otherwise be used by the private.
Or in other words when the government is increasing its expenditure private expenditure comes down. Resource and financial and there are two stages of crowding out. 84 Wernik 2011 p.
There are two types of crowding out. A high interest elasticity of money demand reduces the effects of a fiscal policy action on the interest. One type frequently discussed is when expansionary fiscal policy reduces investment spending by the private sector.
Changes in the pattern of taxation which keep the pattern of spending unaffected do not affect the intertemporal budget constraint of the. The crowding-out effect is an economic theory that argues that rising public sector spending drives down private sector spending.

Extreme Cases Of The Zero Crowding Out Effect Principles Of Public Finance

How Fiscal Policy Influences Aggregate Demand Ifioque Com

Fiscal Policy And Crowding Out In Trade Cycle Macro Economics
0 Comments